|
How DHCP Server WorksDHCP server is used to centrally allocate TCP/IP configurations to computers automatically without setting it manually. DHCP means Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It saves you plenty of time to set up and manage TCP/IP network especially if you have a big network.
This server can be installed as stand alone server or a built-in feature on most network routers. If your network router does support this feature, you can define a pool of IP addresses and other configurations (subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server) to be allocated to computers. The IP address will be leased for a period of time, therefore unused IP address for the duration of lease will be put back to unallocated pool. If the IP address is actively used, your computer will ask the server to renew the lease. How DHCP Works in Microsoft WindowsIn Microsoft Windows as DHCP client, you usually make following setup on your network card (TCP/IP) properties to retrieve IP address and other configurations automatically from this server.
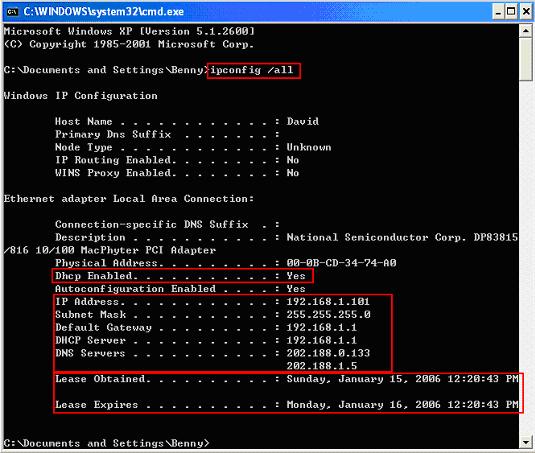
When you switch on your computer, it sends a broadcast packet with DHCP request to the network. This packet will be picked up by the server, which subsequently allocates an IP address and other configurations to the computer. Once the computer is allocated IP address, you can type ipconfig /all on command prompt window to check the network information. It shows you the detail TCP/IP configuration (IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS server). It also shows you the DHCP server is 192.168.1.1, which is my network router in this case (the router I’m using can work as DHCP server). The IP address is leased for one day by checking Lease Obtained and Lease Expired information.
Click here to learn how to release and renew IP address from DHCP server. |

Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?